The Impact of Job Burnout on Performance Efficiency of Senior High School Teachers at Shiyan Foreign Language School in Shenzhen, China
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14456/jriie.2025.7คำสำคัญ:
Job Burnout, Performance Efficiency, Teachersบทคัดย่อ
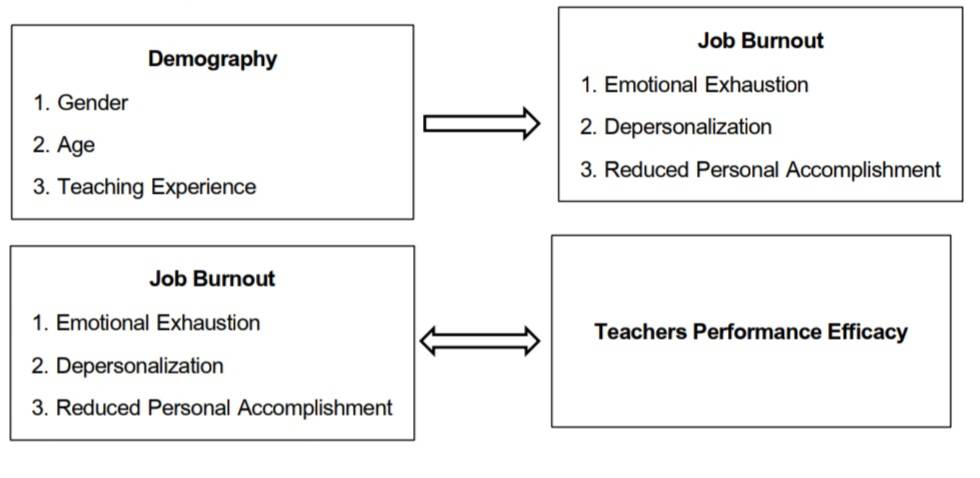
This quantitative study examined job burnout and performance efficiency among 150 senior high school teachers at Shiyan Foreign Language School in Shenzhen, China. The research had three objectives: (1) to assess the level of job burnout, (2) to evaluate the level of performance efficiency, and (3) to examine the relationship between these variables. Data were collected using a questionnaire and analyzed through descriptive statistics (frequency, percentage, mean, and standard deviation) and inferential statistics (correlation and multiple regression analysis). The results revealed that most teachers did not show signs of burnout in terms of emotional exhaustion and depersonalization, but reported a high level of personal accomplishment. Correlation analysis indicated that performance efficiency was negatively related to emotional exhaustion (r = -0.350) and depersonalization (r = -0.749), while personal accomplishment had a significant positive relationship (r = 0.703), all at the 0.01 significance level. Furthermore, regression analysis confirmed that all three dimensions of job burnout significantly influenced performance efficiency at the 0.05 level.
In conclusion, the study demonstrates that emotional exhaustion and depersonalization negatively affect performance efficiency, while personal accomplishment positively enhances it. These findings highlight the predictive role of job burnout in teacher performance and provide practical insights for managing teacher well-being and productivity.
Downloads
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Angus, C. O., & Luna-Angus, L. J. (2023). Job Burnout Affecting Job Performance Among Teaching and Non-Teaching Personnel: Bases for Intervention. American Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Innovation, 2(3), 49–60.
Bakker, A. B., & Demerouti, E. (2007). The Job Demands–Resources model: State of the art. Journal of Managerial Psychology, 22(3), 309–328.
Belay, A. A., Gasheya, K. A., Engdaw, G. T., Kabito, G. G., & Tesfaye, A. H. (2023). Work-related burnout among public secondary school teachers is significantly influenced by psychosocial work factors: A cross-sectional study from Ethiopia. BMC Public Health, 23, 14.
Francisco, C. S., Tupaz, G. B., & Theresa, M. (2024). Teacher Burnout: The Lived Experiences of Teachers with Ancillary Tasks in a National High School in Leyte. American Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Innovation, 3(4), 183–190.
Gao, Y. (2024). Psychosocial work environment, stress, and burnout among Chinese college teachers. International Journal of Research Studies in Psychology, 10(2), 129-145.
Keshavarz, M., & Li, Y. (2023). A Narrative Case History of Distance Education Before, During, and After COVID-19 in China and Iran. Canadian Journal of Learning and Technology, 49(1), 1–15.
Kilonzo, T. M. (2018). Job burnout and performance of teachers in secondary schools in Machakos County in Kenya. The Strategic Journal of Business & Change Management, 5(1), 1–10.
Lu, Y. (2023). High School English Teacher’s Core Competencies in China: A Case Study of the Teacher Qualification Examination Syllabus. BCP Business & Management, 41, 145–151.
Magtalas, S. A. (2024). Teacher’s workload in relation to burnout and work performance. International Journal of Multidisciplinary: Applied Business and Education Research, 5(10), 4111–4123.
Maslach, C., & Jackson, S. E. (1981). The measurement of experienced burnout. Journal of Occupational Behavior, 2(2), 99–113.
Maslach, C., & Leiter, M. P. (2016). Understanding the burnout experience: Recent research and its implications for psychiatry. World Psychiatry, 15(2), 103–111.
Moon, J. W., & Choi, H. Y. (2023). Effect of Work Overload on Job Burnout: The Moderation Effect of Problem-Focused Coping and Job Autonomy. STRESS, 31(3), 106–112.
Siadari, E. S., & Safrin, F. A. (2024). Pengaruh lingkungan kerja dan job burnout terhadap produktivitas kerja karyawan pada PT. Indojaya Agrinusa Medan. ManBiz Journal of Management and Business, 3(2), 331–341.
Sun, W., & Dapat, R. (2024). Unraveling Job Stress, Burnout, and Psychological Capital among Chinese EFL Teachers in Higher Institutions. International Education Studies, 17(5), 29.
Trinkenreich, B., Stol, K.-J., Steinmacher, I., Gerosa, M. A., Sarma, A., Lara, M., Feathers, M., Ross, N. P., & Bishop, K. (2023). A model for understanding and reducing developer burnout. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.00000.
Wang, S., Li, X., & Shen, S. (2024). Secondary education (high school) in China. In Education in China: Policy, Practice and Perspectives. Springer.
Yanna, L., Yang, S., & Lin, Z. (2023). Analysis of the Impact of Job Burnout on Quality and Economic Benefits of Enterprises. Journal of Economics, Management and Trade, 29(9), 23–38.
Zhang, Z. (2023). Comparing secondary education in the UK with high school education in China. Lecture Notes in Education Psychology and Public Media, 18(1), 132–138.
ดาวน์โหลด
เผยแพร่แล้ว
รูปแบบการอ้างอิง
ฉบับ
ประเภทบทความ
สัญญาอนุญาต
ลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 2025 วารสารวิจัยและนวัตกรรมทางการศึกษาอุตสาหกรรม

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความนี้ได้รับการเผยแพร่ภายใต้สัญญาอนุญาต Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ซึ่งอนุญาตให้ผู้อื่นสามารถแชร์บทความได้โดยให้เครดิตผู้เขียนและห้ามนำไปใช้เพื่อการค้าหรือดัดแปลง หากต้องการใช้งานซ้ำในลักษณะอื่น ๆ หรือการเผยแพร่ซ้ำ จำเป็นต้องได้รับอนุญาตจากวารสาร


